
There are many diseases that manifest themselves as painful sensations in the lumbar region. They may indicate problems with the spine, joints, muscles, internal organs: kidneys, intestines, liver. This is a rather insidious symptom and without visiting a doctor it is impossible to determine the true cause of pain in the lower back. Correct treatment is only possible after diagnosis in a medical institution.
types of pain
During the initial examination, the doctor should ask the patient about the nature of the pain. In duration they can be:
- sharp- occur suddenly, paroxysmally, differ in intensity and last less than 1 month;
- subacute- the last 2-3 months, most often they are recurrent: they activate for 2-5 days, then disappear and return after a while;
- chronic- last more than 1 year, the course is usually recurrent.
Doctors have found that most often chronic pain in this area is associated with the formation of local muscle spasms, compactions that have certain pain points (the so-called myofascial syndrome). The process also involves the muscles that straighten the spine, the muscles of the buttocks, the pelvic ligaments, and the sacroiliac joint.
The nature of the pain is sharp, aching and dull. By intensity: strong, medium, weak. Depending on the location of the pain, the following types are distinguished:
- lumbodynia- pain in the lumbar or lumbosacral region;
- sciatica- in the lumbar area, which radiates towards the leg;
- sacralgia- in the sacral area;
- coccydynia- in the tailbone.
5 facts about low back pain
- Approximately 25% of all clinic visits for back pain are related to sensations in the lumbar region.
- According to research, 84% of people have experienced pain in the lower back at least once in their lives.
- Between 44% and 78% of patients (depending on age and region of residence) experience repeated attacks of lumbodynia.
- Up to 37% of people periodically lose their ability to work due to low back pain.
- In 85% of patients who consult a doctor for pain in the lumbar region, musculoskeletal disorders are identified, which become the cause of pain.
- According to statistics, about 90% of patients with acute pain in the lumbosacral region recover within 2 weeks.
Causes of low back pain.
Musculoskeletal disorders
In 2006, the European Federation of Neurological Societies officially adopted the following classification of causes of low back pain. They are divided into 3 main groups:
- Compression of the spinal root, peripheral nerve of the lumbar spine. It occurs due to protrusion (degenerative changes) of the intervertebral discs. Less frequently, due to dysplasia (alterations in the formation process) of the upper articular processes of the sacrum.
- Spinal diseases caused by tumors, joint damage, infection, compression fractures, allergic reactions, autoimmune inflammatory processes.
- Musculoskeletal disorders as a result of subluxation, sprain of spinal ligaments, muscle strain, intervertebral joint dysfunction.
Pathologies of internal organs.
- Disorders of the genitourinary system.
Diseases of the urinary system (urolithiasis, cystitis, pyelonephritis) often cause discomfort in the lumbar region.
Low back pain in women may indicate dysfunction of the genital organs. Most often, the main sensations are concentrated in the lower abdomen and radiate to the lumbosacral spine. They can appear during menstruation or after sexual relations.
One of the possible causes of low back pain in women is ovarian tumors, which are located in the back of the uterus. Often, discomfort in the lower back becomes a symptom of uterine fibroids. As it grows, the pain can manifest itself intensely and sharply and indicate serious disturbances in blood supply, stretching of the peritoneum and compression of the nerve plexuses in the pelvic area.
Another cause of low back pain in women is pelvic organ prolapse. In this case, the sensations are of a tight nature. During walking and physical work, its intensity increases.
- Gastrointestinal tract disorders.
Most often, pain is felt in the lumbar region due to gastric and duodenal ulcers and acute pancreatitis. Patients complain that there is a waist-type pain. Usually, the lower back begins to hurt simultaneously with the right/left hypochondrium, where the most intense sensations are concentrated. In several clinical cases, low back pain accompanies an attack of acute appendicitis, although they are not the main symptoms of this disease. Various inflammations of the intestinal mucosa (proctitis, sigmoiditis) can also cause pain.
10 risk factors for low back pain
- Congenital pathologies of the lumbosacral spine.
- Heavy physical work associated with stress on the lower back, frequent bending and vibrations.
- Acute and chronic stress that causes muscle spasms.
- Sedentary lifestyle and prolonged stay in an unnatural position with load on the lumbar region.
- A weak muscular corset, which causes incorrect posture, stooping, scoliosis and kyphoscoliosis.
- Metabolic disorders and excess body weight, which increases the load on the lower spine.
- Increased physical activity and sports participation increase the risk of injury.
- Age over 50 years: due to the development of degenerative processes in the spine.
- Frequent stress, depression.
- Poor nutrition with lack of vitamin B.
Low back pain as a symptom of various diseases.
Osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine.
One of the most common diseases whose symptom is pain in the lumbar region. In osteochondrosis, the intervertebral discs, which perform a shock-absorbing function between the vertebrae, become thinner. Nerve roots are compressed, muscles spasm, and intense sharp pain occurs. Its intensity increases when bending over, lifting heavy objects, or when the patient tries to sit up from a lying position or get up from a sitting position.
In advanced cases, a hernia forms between the vertebrae, which only increases the pain. Osteochondrosis most often affects the lumbar spine, as it bears the maximum load when sitting and walking.
A serious complication of osteochondrosis is spondylosis. It is characterized by almost complete destruction of intervertebral discs and the formation of sharp bone protrusions - osteophytes. They damage nearby tissues and cause sharp, intense pain that radiates to one or both legs.
Signs of intervertebral hernia
- The patient can rise from a sitting position only with the support of a chair/table or a knee.
- Any load on the lower back causes an attack of acute pain.
- The patient lies face down, placing only a pillow underneath.
- A person can only pick up an object from the ground by slowly bending down.
Ankylosing spondyloarthritis
The disease arises as a consequence of inflammatory processes in the spine. It is most frequently diagnosed in men between 20 and 35 years old. The patient feels stiffness in the lower back and discomfort in the sacrum in the morning and at rest. Little by little, during the day, this feeling passes, the person "walks. "Many people do not pay attention to this alarming symptom; Meanwhile, ankylosing spondylitis causes a gradual fusion of the vertebrae, decreased spinal mobility, and disability. Therefore, you should consult a doctor at the first signs of illness: morning stiffness in the spine.
spondyloarthrosis
This disease affects the cartilaginous tissue that covers the intervertebral discs. With age, it becomes thinner, destroyed, and bone growths form in places where cartilage breaks down. Due to the fact that the intervertebral discs rub against each other, the nerve roots become irritated; This process is accompanied by intense lower back pain. The muscles in the problem area of the back are constantly tense and in spasm.
Signs of spondylarthrosis
- The pain becomes more intense after exercise and disappears after rest.
- The pain appears after standing or walking for a long time.
- Simultaneously with low back pain, the patient feels discomfort in one of the hips and in the hip joint.
Urolithiasis disease
The pain in this pathology is paroxysmal and very intense. Usually painful sensations arise from the inflamed kidney. The patient finds it difficult to find a position in which he feels better. After attacks, urine takes on a reddish color and its volume decreases.
Inflammation in superficial tissues and fibers.
The cause of the pain may be a carbuncle or boil. These are dense purulent formations on the skin more than 1 cm in diameter, easy to notice due to their purple color. The painful sensations are sharp, intense and pulsating.
Paranephritis, an inflammation of the perirenal tissue caused by infection, is also painful. The sensations become stronger with inhalation and movement. The patient tries to lie down with his legs bent; In this position the pain is less pronounced. The skin in the affected area becomes swollen and red.
Inflammation of the spine, spinal cord.
Osteomyelitis is an inflammatory process in the bone marrow that affects all bone tissue. The acute form is characterized by increasing pain of a pulling and explosive nature. It is combined with signs of intoxication and fever.
Tuberculosis of the spine occurs due to infection with Koch's bacillus. The first signs of the disease can appear many years after infection. It all starts with a deep pain that appears after exercise. The infection affects the vertebrae, making the patient's movements difficult and a characteristic gait is formed.
Other diseases
Low back pain can be a symptom of numerous pathologies, including some quite exotic ones. These include, for example, foot and mouth disease, Ebola fever, hemorrhagic fevers and Japanese mosquito encephalitis.
- Cardiovascular diseases: abdominal aortic aneurysm, Loeffler endocarditis.
- Myositis is inflammation and muscle pain in the lower back, which can be caused by infectious diseases such as influenza, sore throat and even common ARVI.
- Benign and malignant neoplasms of the spine and spinal cord.
- Renal pathologies: glomerulonephritis, renal vein thrombosis, pyelonephritis, cyst.
- Low back pain in men occurs with prostate cancer.
Why does my lower back hurt when I cough?
Coughing causes muscle tension in the affected area, causing pain. Often, patients first become aware of a developing illness when they notice pain when coughing. Most often, these sensations are a sign of:
- intervertebral hernia,
- osteochondrosis,
- neuralgia,
- facet arthropathy,
- kidney diseases.
Diagnosis
As noted above, pain in the lumbosacral region can be a symptom of many diseases. Therefore, to identify objective causes, it is advisable to consult a doctor at the first signs. You can make an appointment with an orthopedic doctor, neurologist, or surgeon. In the future, you may need to see a rheumatologist, urologist, or gastroenterologist.
- Initial examination.The doctor evaluates tissue sensitivity, muscle function, and reflexes in the affected area.
- Bone scan.The examination shows changes in the structure of bones, cartilage and joints.
- Blood and urine tests.With its help, it is possible to determine the presence of infections and inflammatory processes.
- Functional diagnosis. Includes methods for assessing nerve conduction and muscle performance: electroneurography, electromyography.
- CT and MRI.It allows a detailed examination of the state of bone, muscle, nerve and vascular structures.
- UltrasoundIt is carried out if pathology of the pelvic organs, prostate or kidneys is suspected.
It is important to exclude (or confirm the presence of) a tumor, to differentiate between compression of the spinal roots and pain syndrome of a musculoskeletal nature. Based on the diagnostic data, the doctor will determine the true cause of the pain and prescribe an effective treatment program.
Is bed rest necessary?
None of the recommendations for the treatment of low back pain in diseases of the musculoskeletal system contain instructions on strict bed rest. On the contrary, patients are advised to resume normal activities as soon as possible to prevent the formation of chronic pain syndrome. In severe cases, that is, with severe pain, strict immobilization for 1 to 3 days is recommended. For acute pain in the lower back, you can use a fixation belt. However, long-term lumbar fixation is not recommended unless there is trauma or spondylolisthesis. Little by little it is necessary to include special exercises to strengthen the spine and muscles.
Low back pain treatment
In most cases, a combination of medicinal and non-medicinal agents is required to resolve the problem.
Medicine
The basis of drug therapy is non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). They affect the peripheral mechanisms of pain formation and are prescribed for exacerbation of pain syndrome. In most clinical cases, treatment is carried out in courses, no more than 12 weeks.
In most cases, patients are prescribed B vitamins to improve nerve conduction, decongestants and sedatives. In the chronic course of the disease, it is possible to take antidepressants. For severe muscle spasms and pain: muscle relaxants, weak opioids.
No drugs
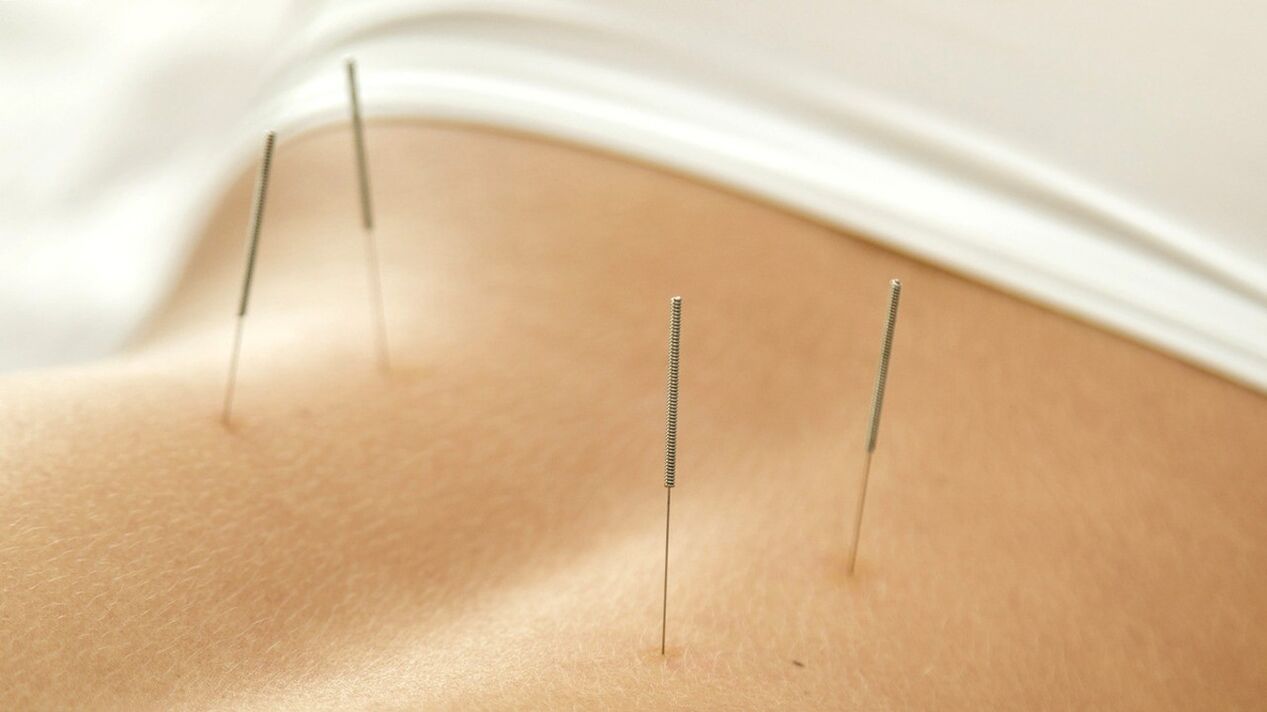
Additionally, the patient may be prescribed manual therapy, acupuncture (acupuncture). The procedures aim to activate metabolism and blood circulation in the affected area. This allows better nutrition of the tissues.
According to doctors, physiotherapy, exercises to strengthen the muscles of the lumbar region, traction therapy and transcutaneous electrical neurostimulation have little effect. In most cases, these procedures are prescribed in the absence of a pronounced effect when taking drugs for 4-6 weeks. There is no scientific evidence of the effectiveness of massage, physiotherapy or the use of various belts.
What to do for prevention
- In the morning, exercise with simple stretching exercises for the spine and muscles.
- Eat rationally, excluding fatty, fried, smoked, salty, spicy products and alcohol.
- Take care of your own weight.
- Drink at least 1. 5 liters of fluid (preferably water) per day.
- Once every 6 months, take a classic massage course.
- Avoid staying in one position for a long time.
Conclusion
Painful sensations in the lumbar region can be a symptom not only of pathologies of the musculoskeletal system, but also of internal organs. Many patients self-diagnose and treat, for example, a muscle strain, although in reality the problem may be inflammation of the kidney. Such treatment only aggravates the situation: a person focuses on a non-existent disease and triggers serious pathology. That is why it is important to seek qualified help and identify the true cause of the pain. Self-prescribing medications is strictly discouraged.
















